今天开始看LevelDB的源码,看了几个大大小小的数据结构,印象深刻的应该是SkipList了,作为一个典型的以空间换时间的有序链表 相比平衡二叉树而言,还是简单了不少的(对于大多数操作需要O(log n)平均时间)。SkipList是一个二维空间的链表。
找了个比较形象的图:
Skip List的定义
SkipList的定义:
- 一个跳表应该有几个层(level)组成;
- 跳表的第一层包含所有的元素;
- 每一层都是一个有序的链表;
- 如果元素x出现在第i层,则所有比i小的层都包含x;
- 第i层的元素通过一个down指针指向下一层拥有相同值的元素;
- 在每一层中,-1和1两个元素都出现(分别表示INT_MIN和INT_MAX);
- Top指针指向最高层的第一个元素。
然后我们看看LevelDB中是如何实现它的。
首先看下层级的定义,LevelDB中定义了一个SkipList最高层级为12。
enum { kMaxHeight = 12 };然后层级越高的链中数据越少,也就是说,从下面数上去,最底下一层我们定义为第0层,它拥有所有的数据,它是一条严格递增的链表, 也是我们传统意义上的链表。如果我们在里面找数据,那需要花去O(n)的时间。
结点Node的定义
在LevelDB中,每一个节点用一个Node对象进行存储。Node的定义很简单,抛去一些原子操作,实际上它就是二维链上某个结点,其中包含了所有层级的信息,我们看下它的定义:
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
struct SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node {
explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) { }
Key const key;
// Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
// add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
Node* Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
// version of the returned Node.
return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].Acquire_Load());
}
void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
next_[n].Release_Store(x);
}
// No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].NoBarrier_Load());
}
void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
next_[n].NoBarrier_Store(x);
}
private:
// Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
port::AtomicPointer next_[1];
};
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key,Comparator>::NewNode(const Key& key, int height) {
char* mem = arena_->AllocateAligned(
sizeof(Node) + sizeof(port::AtomicPointer) * (height - 1));
return new (mem) Node(key);
}这块其实特别少,它最后用了弹性指针的方式来对不同高度的Node进行不同内存的分配(这里的arena是LevelDB中的内存池,附带了对齐的特性,以后介绍),从而达到节省内存和优化对CPU缓存的目的。
插入结点
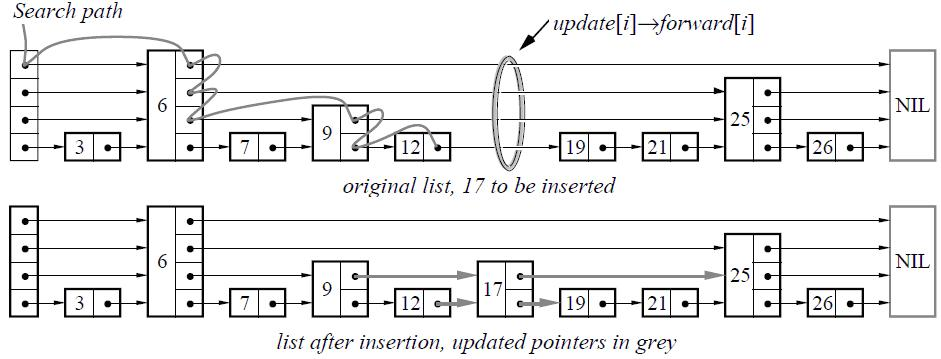
我们来简单看一个插入结点的操作。
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev);
assert(x == NULL || !Equal(key, x->key));
int height = RandomHeight();
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
//fprintf(stderr, "Change height from %d to %d\n", max_height_, height);
// It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (NULL), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since NULL sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
max_height_.NoBarrier_Store(reinterpret_cast<void*>(height));
}
x = NewNode(key, height);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
}这段代码的幽默感其实蛮强= = 我一开始不太理解RandomHeight的意义,后来查了一些资料才知道SkipList就是概率性的进行分层——我获取一个height的随机数,当然它是有要求的,就是在0和kMaxHeight之间,然后,我插入的这个结点就在0-height层上都分布了,同时需要修改前缀的指针(如果超越了当前的max_height_,那么同时也要修改max_height_)。
这里耗费的空间可能是O(n*kMaxHeight)了,然后浪费了这么多资源,目的当然是为了高效的读嘛,我们来看下它的读取操作是怎么做的。
读取Node
这段代码是读取大于等于key的第一个结点(并把所有层级上在key前面的结点记录到prev数组里)
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev)
const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
} else {
if (prev != NULL) prev[level] = x;
if (level == 0) {
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
}
}
}我们的逻辑从最高层开始,我们已知最高层的结点分布是稀疏的,那么利用KeyIsAfterNode函数进行比较。
- 在当前level,如果下一个结点的
key比我要比较的key大,到步骤2。 - 如果到底层了,返回下一个结点,否则降级,再执行1。
因为当前的x结点的下一个层级必然还是x结点,但是它的下一个结点的情况却是未知,因此把低层级的next结点和key进行比较,如此循环,我们就能利用稀疏的链迅速的在密集的链表中找到我们要的元素。
经过整体分析和理解,其实SkipList还是很简单的,最终也是利用了空间换时间的方法。只是它的生成有概率性,但是和平衡二叉树(AVL Tree)比起来,它整体的性价比还是非常可观的~
PS: Google的cpp代码真的很浅显易懂,稍微思考下,做一下笔记,就能明白其中的道理,真的很棒!(也许是LevelDB本身就很简单= =)
欢迎关注我Github 以及 @Gemini

comment 评论区
error_outline 当前评论区已关闭