当我开始接触Tint这个词的时候,其实是蛮不理解它的意思的,以及并不清楚Google发明它的目的,它一般搭配Background配合使用,但是现在已经有了Background,为什么还需要Tint呢?
Tint 翻译为着色。着色,着什么色呢?和背景有关,当然是着背景的色。当我开发客户端,使用了appcompat-v7包的时候,为了实现Material Design的效果,我们会去设置主题里的几个颜色,重要的比如primaryColor,colorControlNormal,colorControlActived 等等,而我们使用的一些组件,比如EditText就会自动变成我们想要的背景颜色,在背景图只有一张的情况下,这样的做法极大的减少了我们apk包的大小。
实现的方式就是用一个颜色为我们的背景图片设置tint(着色)。
例子:
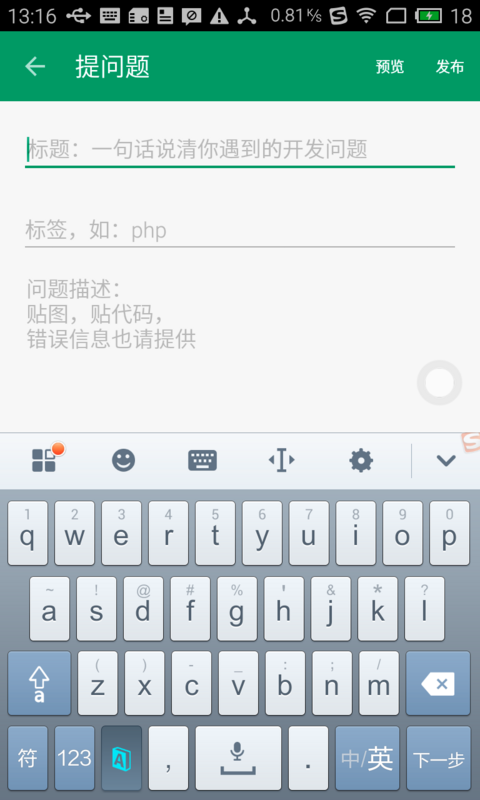
看看即将发布的SegmentFault for Android 2.7中,发布问题功能,这个EditText的颜色和我们的主要颜色相同。它利用了TintManager这个类,为自己的背景进行着色(绿色)。
那么这个原始图是什么样子呢?我们从appcompat-v7包中找到了这个图,是一个.9图,样子如下:
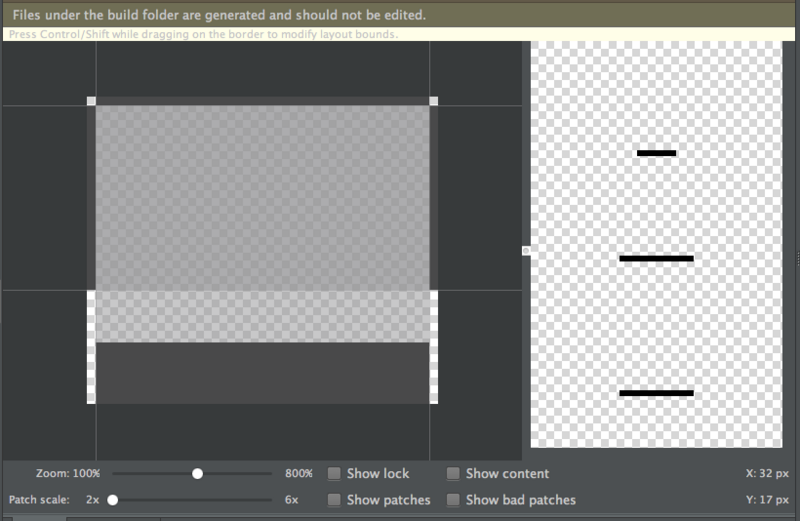
其实它只是一个黑色的条,通过绿色的着色,变成了一个绿色的条。 就是这样的设计方式,使得我们在Material Design中省了多少资源文件呀!
好了,既然理解了tint的含义,我们赶紧看下这一切是如何实现的吧。
其实底层特别简单,了解过渲染的同学应该知道PorterDuffColorFilter这个东西,我们使用SRC_IN的方式,对这个Drawable进行颜色方面的渲染,就是在这个Drawable中有像素点的地方,再用我们的过滤器着色一次。
实际上如果要我们自己实现,只用获取View的backgroundDrawable之后,设置下colorFilter即可。
看下最核心的代码就这么几行
if (filter == null) {
// Cache miss, so create a color filter and add it to the cache
filter = new PorterDuffColorFilter(color, mode);
}
d.setColorFilter(filter);通常情况下,我们的mode一般都是SRC_IN,如果想了解这个属性相关的资料,这里是传送门: http://blog.csdn.net/t12x3456/article/details/10432935 (中文)
由于API Level 21以前不支持background tint在xml中设置,于是提供了ViewCompat.setBackgroundTintList方法和ViewCompat.setBackgroundTintMode用来手动更改需要着色的颜色,但要求相关的View继承TintableBackgroundView接口。
源码解析
看下源码是如何实现的吧,我们以AppCompatEditText为例:
看下构造函数(省略无关代码)
public AppCompatEditText(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(TintContextWrapper.wrap(context), attrs, defStyleAttr);
...
ColorStateList tint = a.getTintManager().getTintList(a.getResourceId(0, -1)); //根据背景的resource id获取内置的着色颜色。
if (tint != null) {
setInternalBackgroundTint(tint); //设置着色
}
...
}
private void setInternalBackgroundTint(ColorStateList tint) {
if (tint != null) {
if (mInternalBackgroundTint == null) {
mInternalBackgroundTint = new TintInfo();
}
mInternalBackgroundTint.mTintList = tint;
mInternalBackgroundTint.mHasTintList = true;
} else {
mInternalBackgroundTint = null;
}
//上面的代码是记录tint相关的信息。
applySupportBackgroundTint(); //对背景应用tint
}
private void applySupportBackgroundTint() {
if (getBackground() != null) {
if (mBackgroundTint != null) {
TintManager.tintViewBackground(this, mBackgroundTint);
} else if (mInternalBackgroundTint != null) {
TintManager.tintViewBackground(this, mInternalBackgroundTint); //最重要的,对tint进行应用
}
}
}
然后我们进入tintViewBackground看下TintManager里面的源码
public static void tintViewBackground(View view, TintInfo tint) {
final Drawable background = view.getBackground();
if (tint.mHasTintList) {
//如果设置了tint的话,对背景设置PorterDuffColorFilter
setPorterDuffColorFilter(
background,
tint.mTintList.getColorForState(view.getDrawableState(),
tint.mTintList.getDefaultColor()),
tint.mHasTintMode ? tint.mTintMode : null);
} else {
background.clearColorFilter();
}
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT <= 10) {
// On Gingerbread, GradientDrawable does not invalidate itself when it's ColorFilter
// has changed, so we need to force an invalidation
view.invalidate();
}
}
private static void setPorterDuffColorFilter(Drawable d, int color, PorterDuff.Mode mode) {
if (mode == null) {
// If we don't have a blending mode specified, use our default
mode = DEFAULT_MODE;
}
// First, lets see if the cache already contains the color filter
PorterDuffColorFilter filter = COLOR_FILTER_CACHE.get(color, mode);
if (filter == null) {
// Cache miss, so create a color filter and add it to the cache
filter = new PorterDuffColorFilter(color, mode);
COLOR_FILTER_CACHE.put(color, mode, filter);
}
// 最最重要,原来是对background drawable设置了colorFilter 完成了我们要的功能。
d.setColorFilter(filter);
}以上是对API21以下的兼容。
如果我们要实现自己的AppCompat组件实现tint的一些特性的话,我们就可以指定好ColorStateList,利用TintManager对自己的背景进行着色,当然需要对外开放设置的接口的话,我们还要实现TintableBackgroundView接口,然后用ViewCompat.setBackgroundTintList进行设置,这样能完成对v7以上所有版本的兼容。
实例
比如我现在要对一个自定义组件实现对Tint的支持,其实只用继承下,加一些代码就好了,代码如下(几乎通用):
public class AppCompatFlowLayout extends FlowLayout implements TintableBackgroundView {
private static final int[] TINT_ATTRS = {
android.R.attr.background
};
private TintInfo mInternalBackgroundTint;
private TintInfo mBackgroundTint;
private TintManager mTintManager;
public AppCompatFlowLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public AppCompatFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attributeSet) {
this(context, attributeSet, 0);
}
public AppCompatFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attributeSet, int defStyle) {
super(context, attributeSet, defStyle);
if (TintManager.SHOULD_BE_USED) {
TintTypedArray a = TintTypedArray.obtainStyledAttributes(getContext(), attributeSet,
TINT_ATTRS, defStyle, 0);
if (a.hasValue(0)) {
ColorStateList tint = a.getTintManager().getTintList(a.getResourceId(0, -1));
if (tint != null) {
setInternalBackgroundTint(tint);
}
}
mTintManager = a.getTintManager();
a.recycle();
}
}
private void applySupportBackgroundTint() {
if (getBackground() != null) {
if (mBackgroundTint != null) {
TintManager.tintViewBackground(this, mBackgroundTint);
} else if (mInternalBackgroundTint != null) {
TintManager.tintViewBackground(this, mInternalBackgroundTint);
}
}
}
@Override
protected void drawableStateChanged() {
super.drawableStateChanged();
applySupportBackgroundTint();
}
private void setInternalBackgroundTint(ColorStateList tint) {
if (tint != null) {
if (mInternalBackgroundTint == null) {
mInternalBackgroundTint = new TintInfo();
}
mInternalBackgroundTint.mTintList = tint;
mInternalBackgroundTint.mHasTintList = true;
} else {
mInternalBackgroundTint = null;
}
applySupportBackgroundTint();
}
@Override
public void setSupportBackgroundTintList(ColorStateList tint) {
if (mBackgroundTint == null) {
mBackgroundTint = new TintInfo();
}
mBackgroundTint.mTintList = tint;
mBackgroundTint.mHasTintList = true;
applySupportBackgroundTint();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public ColorStateList getSupportBackgroundTintList() {
return mBackgroundTint != null ? mBackgroundTint.mTintList : null;
}
@Override
public void setSupportBackgroundTintMode(PorterDuff.Mode tintMode) {
if (mBackgroundTint == null) {
mBackgroundTint = new TintInfo();
}
mBackgroundTint.mTintMode = tintMode;
mBackgroundTint.mHasTintMode = true;
applySupportBackgroundTint();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public PorterDuff.Mode getSupportBackgroundTintMode() {
return mBackgroundTint != null ? mBackgroundTint.mTintMode : null;
}
}赶快去试试吧~
欢迎关注我Github 以及 @Gemini

comment 评论区
error_outline 当前评论区已关闭